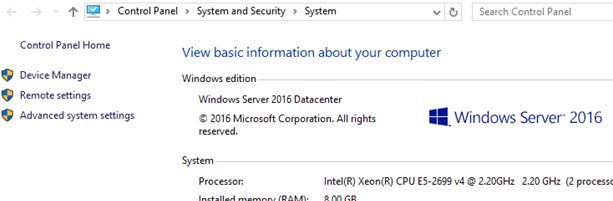
When analyzing the server licenses used in our corporate network (with a KMS server deployed) we found that a more expensive Windows Server Datacenter edition is installed on one of the host. At the same time the server does not use Datacenter features such as virtualization, S2D, Azure Stack, Storage Replica, etc. We had to change (downgrade) the installed Windows Server 2016 Datacenter to Standard edition to save money. We did not consider clean Windows Server reinstallation, because some roles are already configured, and additional software with hardware-related licenses had been installed on the server.
Although Microsoft supports only Windows Server edition upgrade using DISM (see the post on how to convert Windows Server Evaluation to licensed version), you can also perform a reverse procedure and downgrade the Datacenter edition to Standard one keeping all current settings, installed roles and apps.
Important! Officially Microsoft does not support the downgrade of a higher Windows Server edition to a lower one. The officially recommended method is a clean OS installation. So you may follow the steps described below at your own risk.
We strongly recommend to backup your operating system image before performing a downgrade (at least through Windows Server Backup).
Also be very careful when downgrading a Windows Server with the ADDS domain controller role installed. It is better to transfer the FSMO roles and demote it from a DC to domain-member server (before you do it, backup your domain controller and you can restore the DC from a backup in case of any issues).
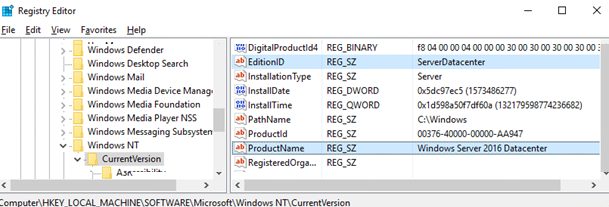
- On a running Windows Server 2016 Datacenter, open the Registry Editor and go to reg key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion;
- Check the values of the following REG_SZ parameters: EditionID = ServerDatacenter, ProductName = Windows Server 2016 Datacenter;
- Change the values as follows:
EditionIDto ServerStandard,ProductNameto Windows Server 2016 Standard;
- Close the rgedit.exe;
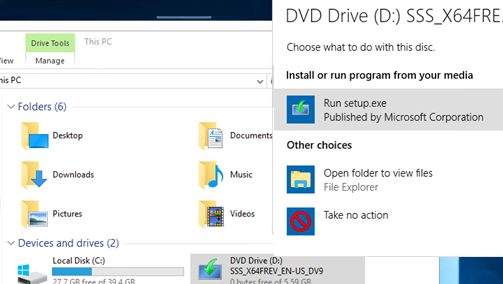
- Mount the installation Windows Server 2016 ISO image and run the setup wizard (setup.exe);

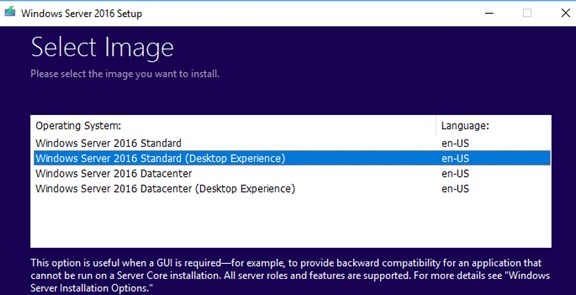
- When selecting the install options in the Windows Server Setup window, select Upgrade and Windows Server 2016 Standard (Desktop Experience) edition;

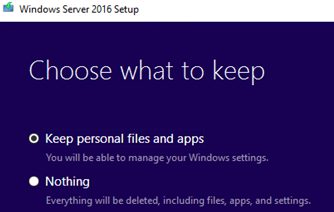
- Check the option Keep personal files and apps;

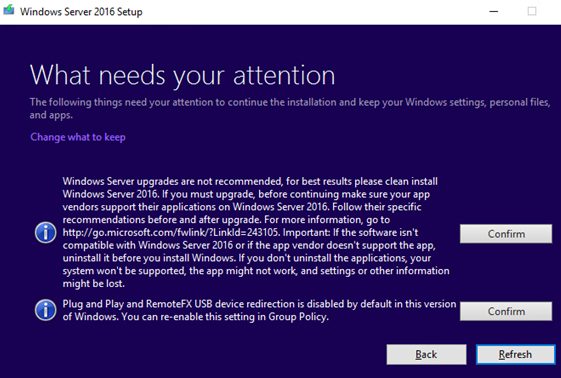
- Click on the Confirm button for items found. In my case, the first item said that a Windows Server upgrade is not recommended, and it was better to clean install the OS, and the second one said that PnP and RemoteFX USB device redirection were disabled in this Windows version by default;

- Start the Windows Server update. Wait till it is over and after several restarts make sure that Windows 2016 Standard edition is now running on the host.

This downgrade method should work for all supported Windows Server versions (2012R2/2016/2019). Also you can use it to downgrade and update the version, for example from Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter to Windows Server 2019 Standard (although it is not recommended either).


Great article, thanks for this. Worked a treat.